Changing The Port Of An ASP.NET Web Application Or API
[ASP.NET, C#, .NET]
When you create a web application (or a web API), a random, available port is allocated to your application.
Let us start by creating a new application
dotnet new web -o TestAPI
We then change to the new directory TestAPI and run the application
dotnet run
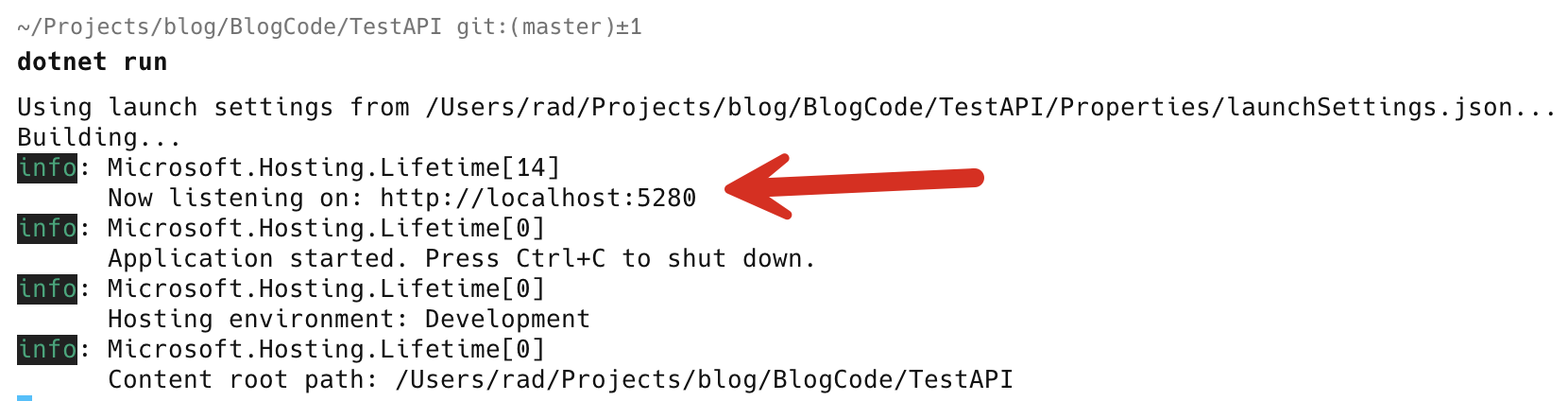
Here you can see the port 5280 was assigned.
You might ask yourself - is this stored anywhere?
Yes.
In your project, there is a Properties folder. Within this is a file named launchSettings.json.
For this project, mine looks like this:
{
"$schema": "https://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json",
"profiles": {
"http": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5280",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"https": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:7286;http://localhost:5280",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
The magic is taking place here:
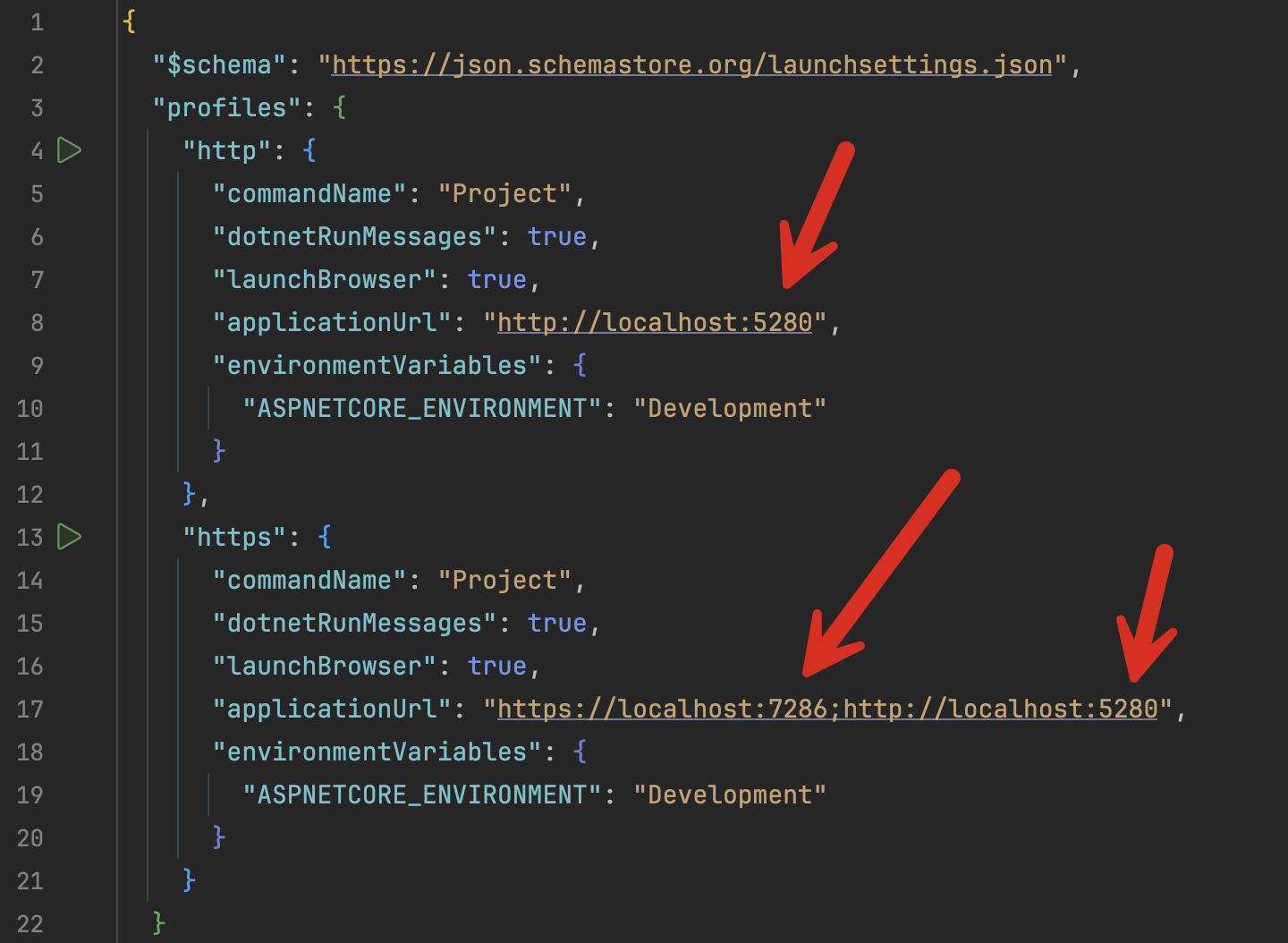
These are the places where the ports are specified.
If you want to change them during the debug stage, change them to an available port and restart your application.
If the project has been deployed, this will not work, as there is no launchSettings.json for deployed files.
In this case you need to make the change to the appsettings.json file.
If you open it, it will look like this:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
To specify the ports to use, add the setting Urls, specifying the protocol and ports you want to use as semicolon delimited strings. Note the plural. Even if you are providing only one, you still say Urls.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"Urls": "http://*:6000;https://*:6001"
}
Here, I am using 6000 for Http and 6001 for Https.
You can also, if you wish, override these in appsettings.Devlopment.json, appsettings.Staging.json or appsettings.Production.json, depending on your needs.
If you run the application now:
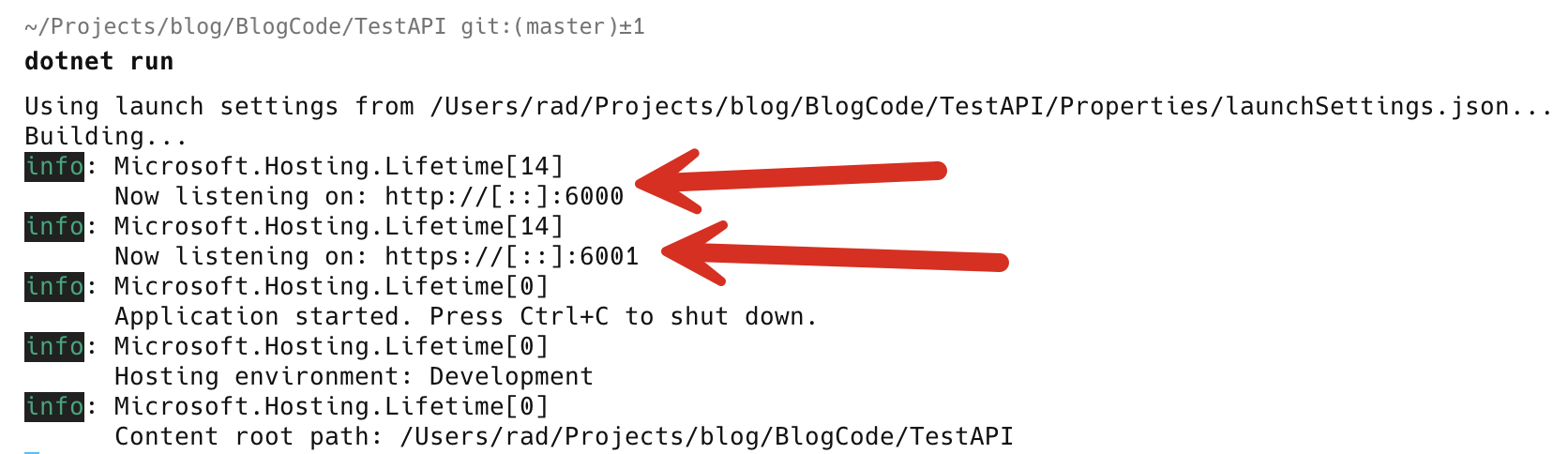
You can also pass the ports you want to use as arguments to the run command.
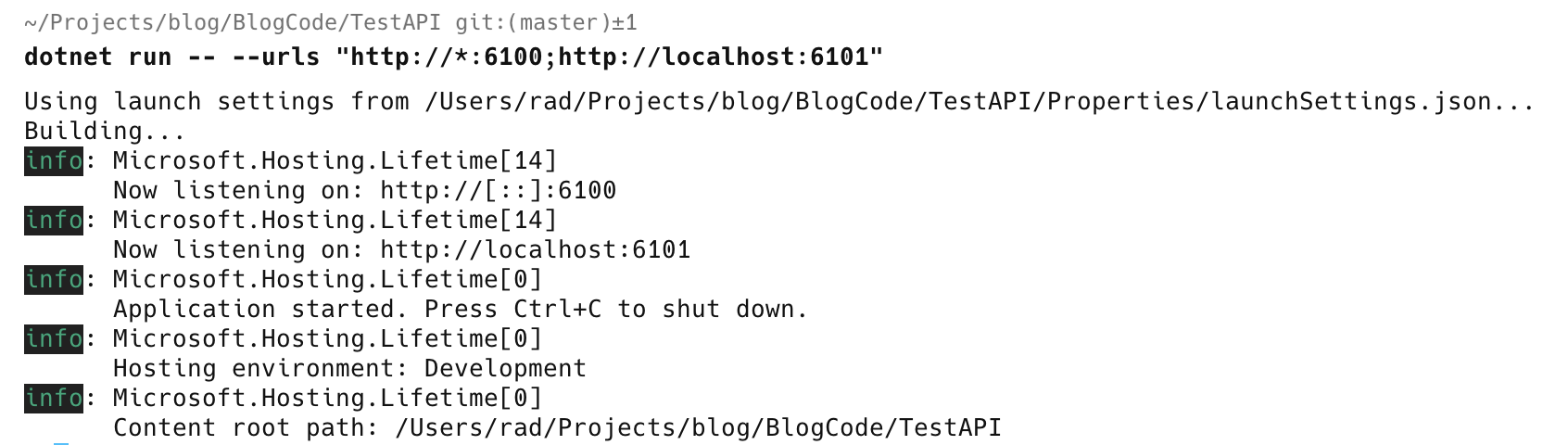
dotnet run -- --urls "http://*:6100;http://localhost:6101"
The extra -- it is to make sure that the --urls is treated as a parameter for configuration, and not the dotnet run command itself.
TLDR
You can change the ports a web application is using in 3 ways:
- Change in launchSettings.json
- Change in appsettings.json
- Pass as a command line parameter
The code is in my GitHub.
Happy hacking!